Nguyên công boring
Boring holes
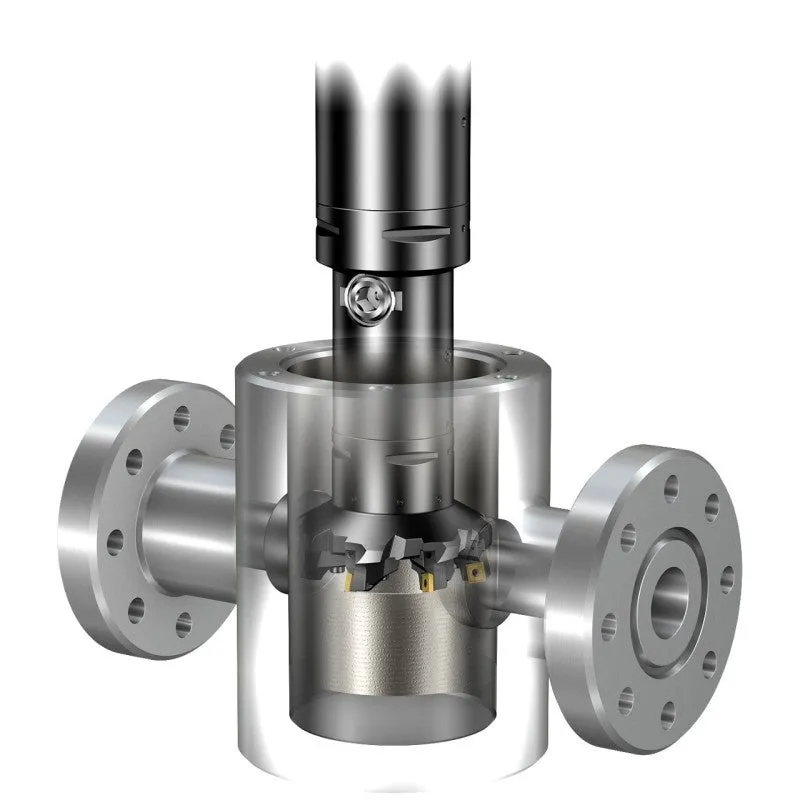

Boring is a machining process for enlarging or improving the quality of an existing hole. When boring holes, there are several flexible tool systems available in a wide diameter range for both rough and fine boring.
Initial considerations for boring holes
These initial considerations will affect the choice of boring tools and how they are applied when boring holes.
The hole
The quality of the hole affects the type of operation and choice of tool.
Consider the hole dimension, limitations and quality demands:
- Boring diameter
- Depth
- Tolerance, surface finish, position and straightness
- Type of hole

Through hole

Blind hole
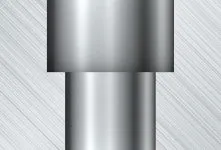
Step hole

Cross hole/ interrupted cut
Identify the type of operation, roughing or finishing:
Roughing
Machining of an existing hole with focus on metal removal in order to prepare for finishing. The existing holes are made by methods such as drilling, casting, forging and flame cutting. For hole tolerances larger or equal to IT9.
Finishing
Machining of an existing hole to achieve a close hole tolerance and high quality surface finish. Small cutting depths, generally below 0.5 mm (0.020 inch). For hole tolerances between IT6 and IT8.

Roughing

Finishing
The component
Identify what type of component to work with.
Shape and quality:
- Does the material have good machinability and chip breaking properties?
- Is the component stable or are there thin sections that can cause vibrations?
- Is a tool extension needed to be able to machine the hole?
- Can the component be fixed properly? What stability problems need to be considered?
- Is the component rotation symmetric around the hole, i.e. can the hole be machined in a turning lathe?
- Batch size – mass production, which justifies an optimized engineered tool to maximize productivity, or machining a single hole?
Material:
- Machinability
- Chip breaking
- Hardness
- Alloy elements
The machine

Important machine considerations:
- Spindle interface
- Machine stability
- Spindle speed (rpm), is it enough for small diameters?
- Coolant supply and pressure, are coolant volume and pressure enough?
- Clamping of the workpiece, is the stability sufficient?
- Horizontal or vertical spindle? A horizontal spindle enables better chip evacuation
- Power and torque, is the power enough for large diameters and for a three cutting edge boring tool?
- Tool magazine, is there limited space?

Bài viết khác
Tiện các loại vật liệu khác nhau
27/02/2025
Sử dụng nước làm mát trong gia công tiện
27/02/2025
Cách lựa chọn dao tiện
27/02/2025
Tăng tuổi thọ dao tiện
27/02/2025
Phương pháp đạt chất lượng sản phẩm tiện
27/02/2025






