Tiện ngoài
External turning
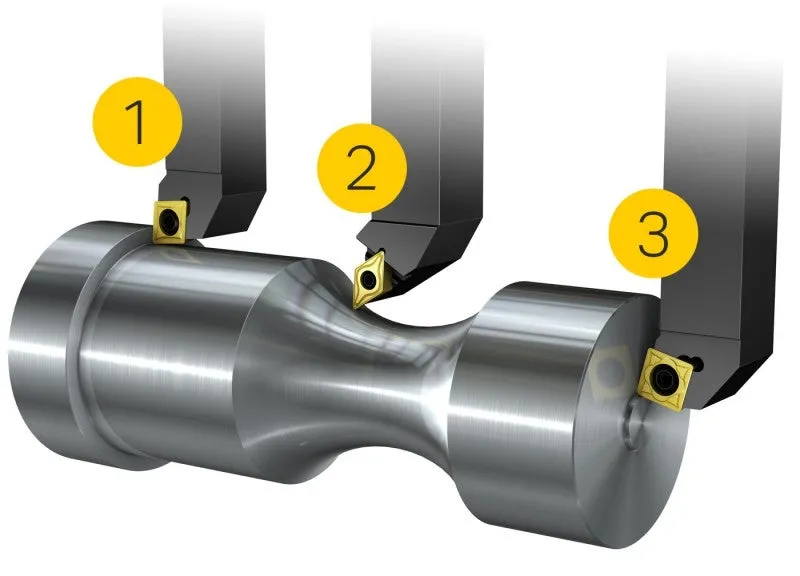
External turning operations machines the outer diameter of the workpiece. Since external turning is one of the most well-known and commonly used process, demands on chip control, process security and component quality are high. The basic application areas for external turning are longitudinal turning (1), profile turning (2), and face turning (3).
With PrimeTurning™ you can do turning in all directions, with faster metal removal rates and the highest productivity.
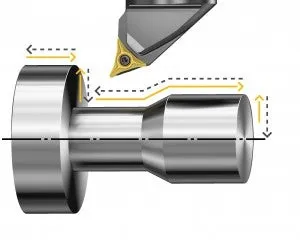
Longitudinal turning

For longitudinal turning, the feed movement of the tool is along the axis of the workpiece, which means the diameter of the part will be turned down to a smaller size. This is the most common turning operation.
When choosing a tool for longitudinal turning it is recommended to choose the clamping system of the insert in the tool holder first. What to choose is determined by the type of operation and, to some extent, the size of the workpiece. Roughing operations on large workpieces has considerably different demands than finishing operations on small components.
Insert shape
The largest suitable insert nose angle should be selected for strength and cost efficiency.
Entering angle
The entering angle of the tool affects the chip formation. At an entering angle of 90° (lead angle of 0°), the chip thickness is the same as the feed, fn. A smaller angle, 75–45° (15–45° lead angle), will reduce chip thickness and enable an increase in feed.
Tool holder
If there is a shoulder to machine in the component, use a tool with 91–95° entering angle (-1 to -5° lead angle). Use a C-style (80°) insert as first choice.
A D-style (55°) insert will allow profiling or undercuts.
If there is no shoulder to be machined, productivity can be increased by selecting a square insert and a 75° entering angle (15° lead angle).



Turning tools for longitudinal turning
Profile turning

In profile turning, the cut can vary with regard to cutting depth, feed and speed. Tools used for profile turning are subjected to large variations in stress and depth of cut due to the varying machining directions and diameter changes. One of the most important properties of a profiling tool is accessibility.
Insert shape
The largest suitable nose angle on the insert should be selected for strength and cost efficiency, but the insert nose angle has to be considered in relation to accessibility. The most frequently used nose angles are 35° and 55°.

Entering angle

Analyze the workpiece profile in order to select the most suitable entering angle. A free cutting angle of at least 2° between the workpiece and the insert has to be maintained. However, for reasons relating to surface finish and tool life, at least 7° entering angle (83° lead angle) is recommended.
Tool holder
First choice is a tool with 93° entering angle (-3° lead angle) and a D-style (55°) insert. If a larger ramping angle is needed, use a V-style (35°) insert.
For the possibility to profile in another direction or to make a corner relief, choose a holder with a 107–117° entering angle (-17 to -27° lead angle).Turning tools for profile turning
Face turning

In face turning, the tool is fed radially towards the centre, at the end of the workpiece. The radial cutting forces are high, which may generate deflection on the component and may sometimes also cause vibration.
Insert shape
The insert shape should be selected according to the required entering angle and in relation to the accessibility or versatility required for the workpiece. The largest suitable nose angle on the insert should be selected for strength and cost efficiency.
Entering angle

75° entering angle (15° lead angle)
A reduction of the entering angle, (increasing of the lead angle) can redirect some of the radial forces axially toward the chuck for better stability and reducing vibration tendency.
Tool holder
For optimization, choose a holder with a square insert and a 75° entering angle (15° lead angle).
For versatility, choose a holder with a rhombic 80° or trigon insert and a 95° entering angle (-5° lead angle).Turning tools for face turning
Bài viết khác
Tiện các loại vật liệu khác nhau
27/02/2025
Sử dụng nước làm mát trong gia công tiện
27/02/2025
Cách lựa chọn dao tiện
27/02/2025
Tăng tuổi thọ dao tiện
27/02/2025
Phương pháp đạt chất lượng sản phẩm tiện
27/02/2025






